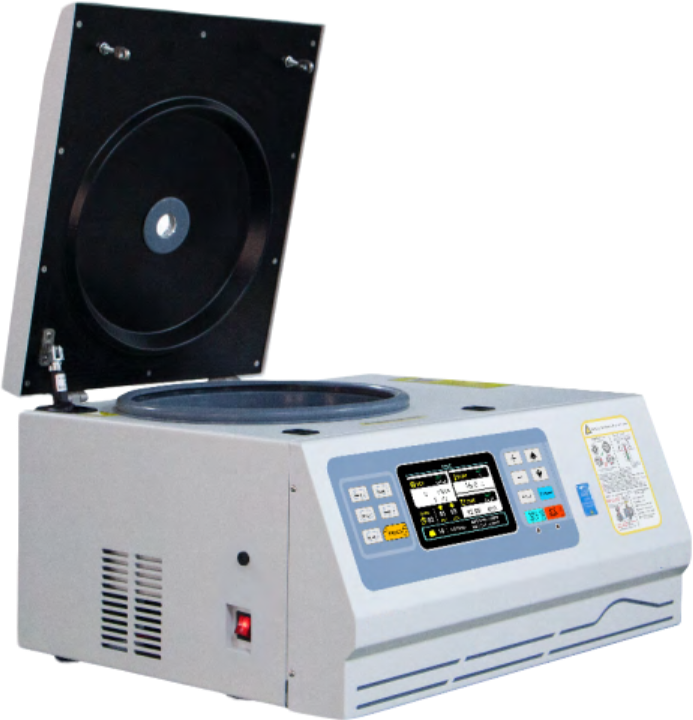
Refrigerated Centrifuge
⭐ The function of a centrifuge is to use centrifugal force to separate,concentrate, or purify substances.
⭐ A refrigerated bag centrifuge is a specially designed centrifuge used for low-temperature centrifugation of frozen bags, particularly blood component bags. It is commonly used for the separation and purification of blood and temperature-sensitive biological samples.
⭐ With a maximum speed of 5500rpm and a maximum RCF of 5952 xg,it meets a wide range of experimental and separation needs.
⭐ The core performance of a centrifuge depends not only on the main unit itself but also heavily on the type and performance of the rotor it is equipped with.
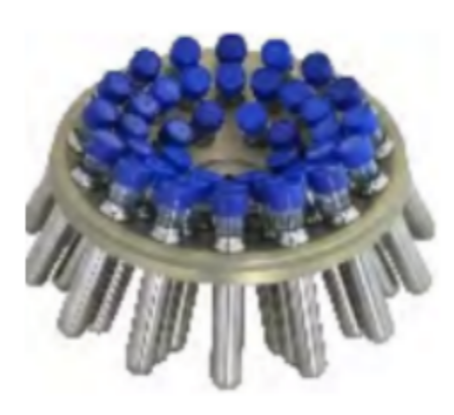 Angle Rotor:
Angle Rotor:
The centrifuge tubes are held at a constant angle relative to the central axis.
As shown in the diagram, each tube fits into a fixed slot, and the angle cannot be adjusted.
The smaller the angle between the centrifuge tube and the rotor axis, the higher the centrifugation efficiency.
 Swing-out Rotor:
Swing-out Rotor:
In this design, the buckets swing out during rotation rather than remaining fixed.
Initially in a vertical position, the buckets swing out to a horizontal position as the rotor spins,
allowing the sample to experience centrifugal force and sediment accordingly during this motion.
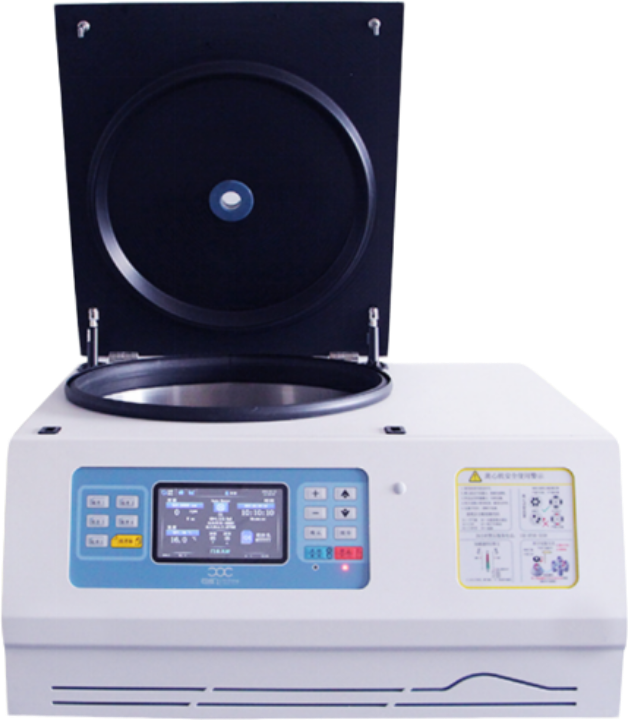

⭐ The key technical specifications of a refrigerated centrifuge usually include:
1️⃣ Maximum Speed (RPM- Revolutions Per Minute):
This indicates the highest speed the rotor can reach. A higher RPM generally means better separation efficiency, but the sample's tolerance must also be considered.
2️⃣ Maximum Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF):
RCF reflects the actual centrifugal force more accurately than RPM. It has a direct effect on how fast and how well the particles in the sample are separated.
3️⃣ Temperature Range:
Typically from -20'C to +40'C. A refrigerated centrifuge can maintain low temperatures to prevent heat buildup during spinning, which helps protect temperature-sensitive samples from degradation.