Endoscopy towers are essential tools in modern minimally invasive surgeries like laparoscopy, hysteroscopy, and thoracoscopy. This guide explains everything you need to know about endoscopy towers—including their components, functions, workflow, and maintenance.
1. Endoscopy Tower: Definition and Use
An endoscopy tower is a modular system that includes all the equipment needed to perform endoscopic procedures. It offers a clean and organized structure for devices such as:
·A surgical video camera system
·A cold light source
·A CO₂ insufflator
·A high-frequency electrosurgical unit (ESU)
These components allow surgeons to perform precise and safe procedures through small incisions.

2. Key Components of an Endoscopy Tower
Here’s what a standard endoscopic imaging tower usually includes:
·Video Camera System (scope, camera head, processor, HD/4K monitor)
·Electrosurgical Unit (ESU)
·CO₂ Insufflator for abdominal expansion
·Medical Cold Light Source
Optional: suction/irrigation pump, image recording module, integrated control panel
Each unit plays a vital role in enabling accurate, high-precision surgery.
3. Electrosurgical Unit (ESU): Precision Cutting and Coagulation
The electrosurgical unit allows for both tissue dissection and bleeding control. It provides:
·Monopolar and bipolar modes
·Power settings based on tissue type
·Built-in safety features (e.g., grounding, auto shutoff)
Ideal for laparoscopic coagulation, tissue dissection, and bloodless surgery.

4. Video Imaging System: Enhanced Surgical Visibility
A 4K endoscopic video system enhances visual clarity during procedures. Compared to HD systems, 4K provides:
·Sharper detail of blood vessels and nerves
·Better color differentiation
·Real-time, high-frame-rate display
This is crucial for identifying critical structures during surgery.
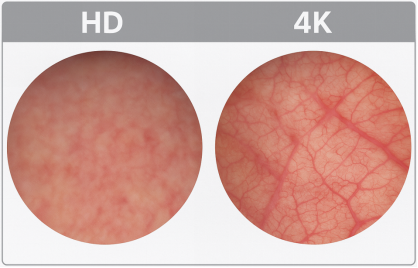
-- 4K and HD comparision
5. Cold Light Source: Illumination Without Heat
Cold light—typically from LED or xenon bulbs—is transmitted via fiber optic cables into the body cavity. It provides:
·High brightness with minimal heat
·Adjustable intensity
·Stable color temperature
This ensures safety while maintaining optimal visibility.
6. CO₂ Insufflator: Creating Operative Space
Used in laparoscopic surgery, the insufflator inflates the abdominal cavity with CO₂ gas. It provides:
·Controlled flow and intra-abdominal pressure
·Leak detection and emergency cutoffs
·Integrated heating in some systems for patient comfort
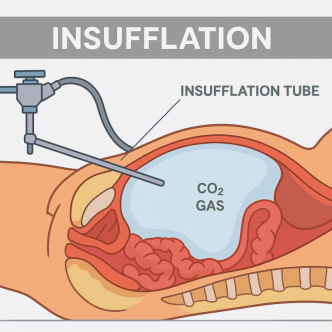
-- Insufflation
7. Optional Add-ons for Advanced Procedures
Modern endoscopy towers may include:
·Suction/Irrigation Pumps
·Recording and Broadcasting Systems
·Touchscreen or voice-controlled hubs
·AI-assisted features or integration with robotic systems
These features support both surgical precision and medical education.
8. Operating Workflow: From Setup to Shutdown
A typical workflow includes:
A. Pre-op equipment check
B. White balance and focus calibration
C. Parameter configuration for HFU and insufflator
D. Sterilization and disinfection post-op
All actions follow strict protocols to ensure patient safety and device longevity.
9. Maintenance & Safety Checklist
To keep the endoscopy tower in top condition:
·Set ESU and insufflator parameters individually
·Clean and sterilize scopes, light cables, and optics
·Calibrate video and light systems regularly
·Learn emergency protocols for device failure
✅ Consider placing this as a printable checklist for OR staff.
10. Trends in Endoscopic Tower Technology
The future of endoscopy towers includes:
·Ultra-HD (8K) and 3D imaging
·Smart integration and cloud storage
·Robotic-assist interfaces
·Live streaming for remote surgery guidance
These advancements will further revolutionize digital surgery and interconnected ORs.
Conclusion
The endoscopy tower is the backbone of modern endoscopic surgery. It integrates imaging, lighting, surgical energy, and gas control into one efficient unit. Whether you're a surgeon, nurse, or medical equipment manager, understanding this system is essential for safe and effective procedures.