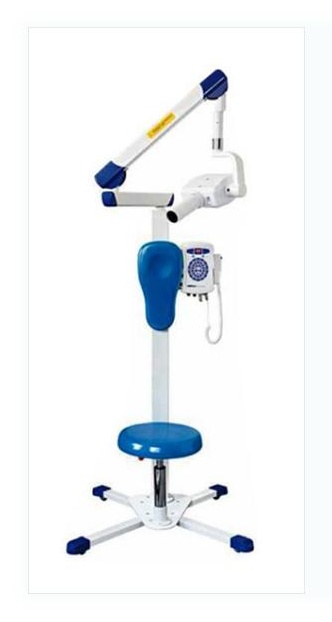
Application of Dental X-ray
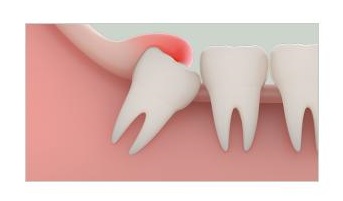
Impacted Tooth Diagnosis
Checking whether wisdom teeth or other teeth are impacted (unable to emerge normally), to determine whether removal is necessary.
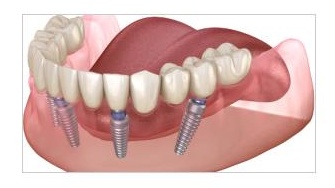
Dental lmplant Planning
Assessing bone density and volume before a dental implant procedure to determine the implant's position and angle.
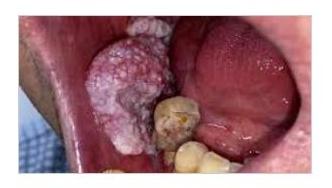
Lesion and Tumor Detection
Detecting cysts, infections, tumors, or other abnormal structures around the teeth or jawbone.
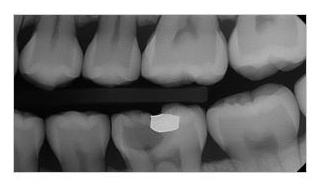
Post-treatment Follow-up
Verifying the effectiveness of dental treatments, such as the sealing after root canal therapy or recovery after dental implants.
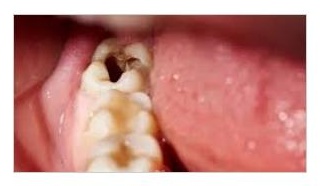
Cavity (Tooth Decay) Diagnosis
Detecting cavities inside the teeth that are difficult to see with the naked eye, especially those hidden between teeth or within the tooth structure.
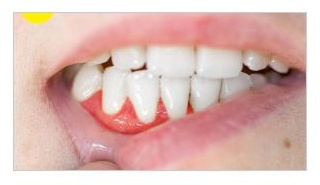
Periodontal Disease Check
Helping assess the health of the bone around the teeth to determine if bone loss or other issues related to periodontal disease exist.
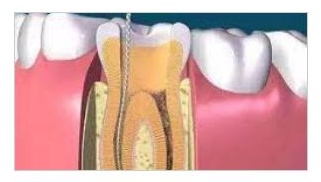
Root Canal Treatment Assistance
Using X-ray imaging to determine the shape, length, and affected areas of the root canals,guiding the root canal treatment process.
Tooth Position and Alignment Check
Analyzing the position and alignment of teeth, particularly when planning for orthodontic treatment.
Dental X-ray
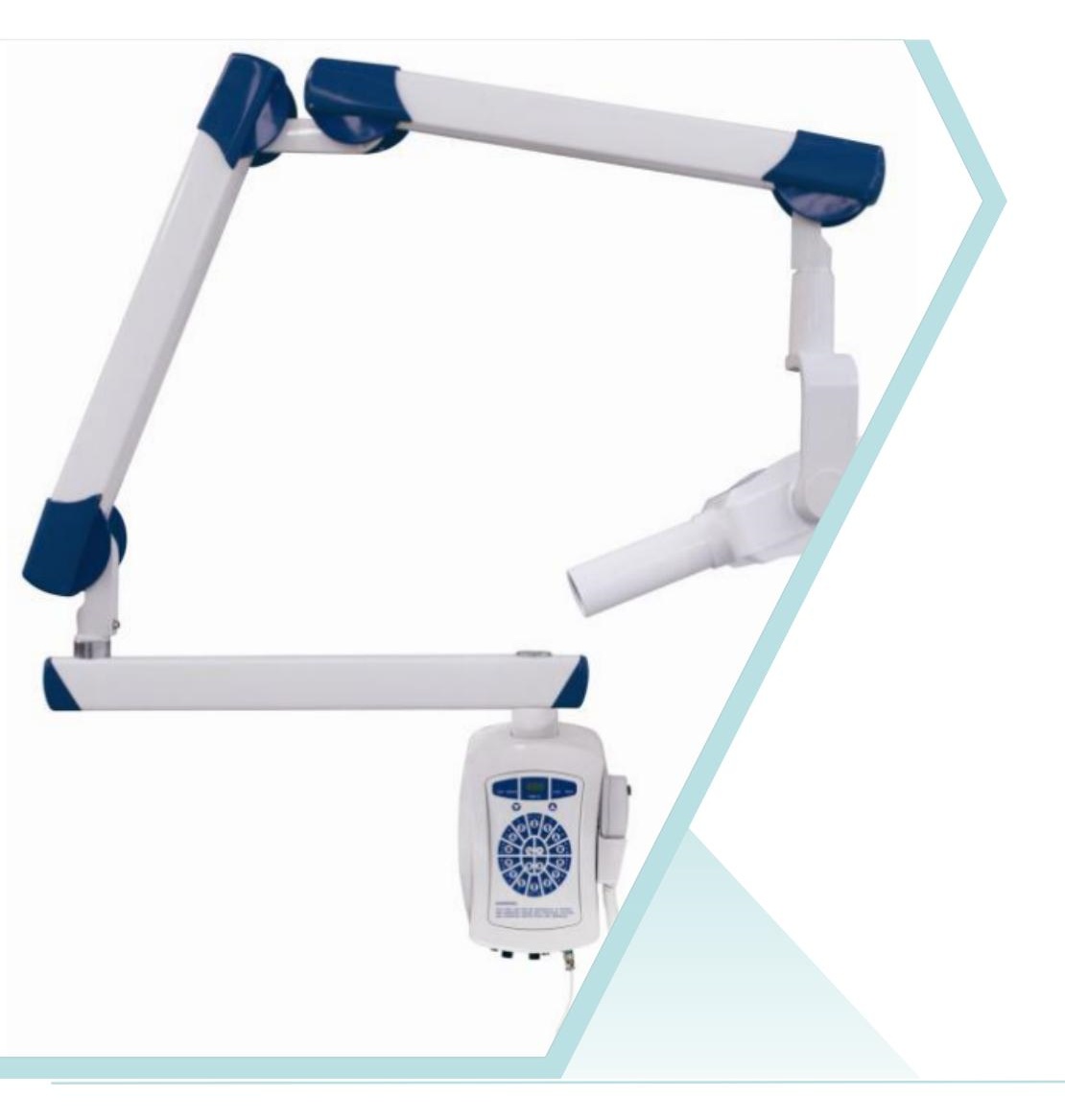

Technical Principle
A dental X-ray is based on the use of X-rays, a form of electromagnetic radiation.which pass through soft tissues and are partially absorbed by denser structures like teeth and bones. This creates a contrast image on a detector or film, allowing detailed visualization of the internal structures of the mouth.
Main Type of Dental X-ray
Floor - Standing Dental X-Ray machine
Wall Mounted Dental X-Ray Machine
Dental CBCT 3D Panoramic X-ray Machine